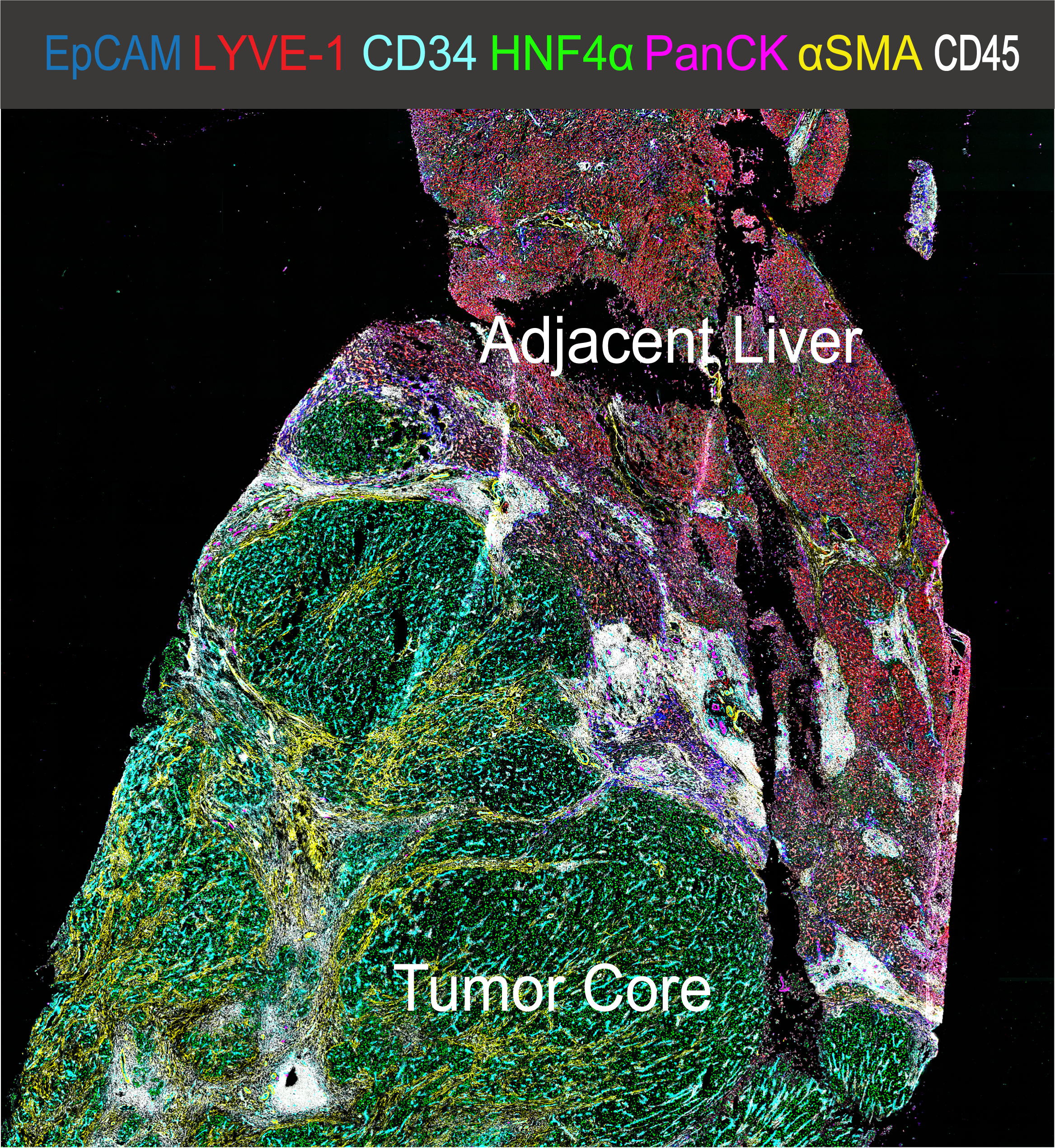
CODEX imaging of HCC | Highly multiplexed spatially resolved immune cell atlas of hepatocellular carcinoma
DOI: 10.7937/BH0R-Y074 | Data Citation Required | 1.4k Views | 1 Citations | Image Collection
| Location | Species | Subjects | Data Types | Cancer Types | Size | Status | Updated | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Liver | Human | 15 | Histopathology, CODEX images, Whole Slide Image, Diagnosis, Demographic, Measurement, Treatment | Hepatocellular carcinoma | Clinical | Public, Complete | 2023/05/30 |
Summary
Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HCC) is a leading cause of cancer-related death and can be considered a prototype of inflammation-derived cancer arising from chronic liver injury. The cell composition of the HCC tumor immune microenvironment (TiME) has a major impact on cancer biology as the TiME can have divergent capacities on tumor initiation, progress, and response to therapy. Recent development of multi-omics and single-cell technologies help us to comprehensively quantify the cellular heterogeneity and spatial organization of the TiME and to further our understanding of antitumor immunity. Multiplexed immunofluorescence microscopy was used to analyze immune cell infiltration in primary human liver cancer samples. We developed and validated a comprehensive 37-plex antibody panel for immunofluorescence imaging of human fresh frozen HCC samples. We applied highly multiplexed co-detection by indexing (CODEX) technology to simultaneously profile in situ expression of 37 proteins at sub-cellular resolution in 15 HCC patient samples (as well as one spleen and one lymph node specimen from anonymous deceased donors for validation purposes) using whole slide scanning. We established an image analysis pipeline to quantify all major cell populations in the human liver using supervised manual gating and unsupervised clustering algorithms. This extremely high-dimensional dataset was generated to allow data-driven investigation in patho-physiological immune cell interactions in the context of HCC. Clinical metadata including TMN stage, sex, ethnicity, pretreatment, and histopathological reports are available for all patient samples. Using high-dimensional spatially resolved quantitative analysis of multiplexed immunofluorescence microscopy images, we generated a unique dataset and profiled the single-cell pathology landscape for human HCC. In situ phenotyping of 4,500,000 single cells (including 1,500,000 CD45+ immune cells) allowed for the quantification of cell phenotype clusters, differential analysis of activation markers and spatial features of each individual cell. CODEX imaging revealed detailed composition of the immune cell niche in human liver cancer tissue allowing for further distinct spatial Beyond that, whole slide imaging allowed for the identification of the tumor-to-liver interface as a unique site of immune cell inhibition. Here, we demonstrate that spatially resolved, single-cell analysis of human liver cancer tissue allows for the in-depth characterization of the immune cell composition of HCC. This tool can be used for biomarker research, to determine cellular functional states in intact tissue and to spatially and functionally quantify interactions between immune cells in the context of hepatocarcinogenesis. We expect that making this dataset publicly available will stimulate broad research endeavors into the immune tumor microenvironment of HCC and allow computational scientists to discover new biomarkers and features. Further details on the study can be obtained in our paper. The files are labeled according to the following system: Introduction:
Methods:
Results:
Discussion:
Glossary:
Data Access
Version 1: Updated 2023/05/30
| Title | Data Type | Format | Access Points | Subjects | License | Metadata | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tissue Slide Images | Histopathology, CODEX images, Whole Slide Image | TIFF | Download requires IBM-Aspera-Connect plugin |
15 | 646 | CC BY 4.0 | — | ||
| Clinical data | Diagnosis, Demographic, Measurement, Treatment | XLSX | 15 | CC BY 4.0 | — |
Citations & Data Usage Policy
Data Citation Required: Users must abide by the TCIA Data Usage Policy and Restrictions. Attribution must include the following citation, including the Digital Object Identifier:
Data Citation |
|
|
Ruf, B., Bruhns, M., Babaei, S., Kedei, N., Heinrich, B., Subramanyam, V., Qi, J., Greten, L., Ma, C., Wabitsch, S., Green, B., Bauer, K., Myojin, Y., Benmebarek, M.-R., Nur, A., McCallen, J., Pouzolles, M. C., Kleiner, D. E., Telford, W., … Greten, T. F. (2023). Highly multiplexed spatially resolved immune cell atlas of hepatocellular carcinoma (CODEX imaging of HCC) (Version 1) [Data set]. The Cancer Imaging Archive. https://doi.org/10.7937/BH0R-Y074 |
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Intramural Research Program of the NIH, NCI (ZIA BC 011345)
Related Publications
Publications by the Dataset Authors
The authors recommended the following as the best source of additional information about this dataset:
- Ruf B, Bruhns M, Babaei S, Kedei N, Ma L, Revsine M, Benmebarek MR, Ma C, Heinrich B, Subramanyam V, Qi J, Wabitsch S, Green BL, Bauer KC, Myojin Y, Greten LT, McCallen JD, Huang P, Trehan R, Wang X, Nur A, Murphy Soika DQ, Pouzolles M, Evans CN, Chari R, Kleiner DE, Telford W, Dadkhah K, Ruchinskas A, Stovroff MK, Kang J, Oza K, Ruchirawat M, Kroemer A, Wang XW, Claassen M, Korangy F, Greten TF. Tumor-associated macrophages trigger MAIT cell dysfunction at the HCC invasive margin. Cell. 2023 Aug 17;186(17):3686-3705.e32. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2023.07.026. PMID: 37595566; PMCID: PMC10461130.
Research Community Publications
TCIA maintains a list of publications that leveraged this dataset. If you have a manuscript you’d like to add please contact TCIA’s Helpdesk.
