NSCLC-Radiomics-Interobserver1 | NSCLC-Radiomics-Interobserver1
DOI: 10.7937/tcia.2019.cwvlpd26 | Data Citation Required | 1.7k Views | 10 Citations | Image Collection
| Location | Species | Subjects | Data Types | Cancer Types | Size | Status | Updated | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lung | Human | 22 | RTSTRUCT, CT, SEG, Demographic, Diagnosis | Non-small Cell Lung Cancer | Clinical | Public, Complete | 2020/08/31 |
Summary
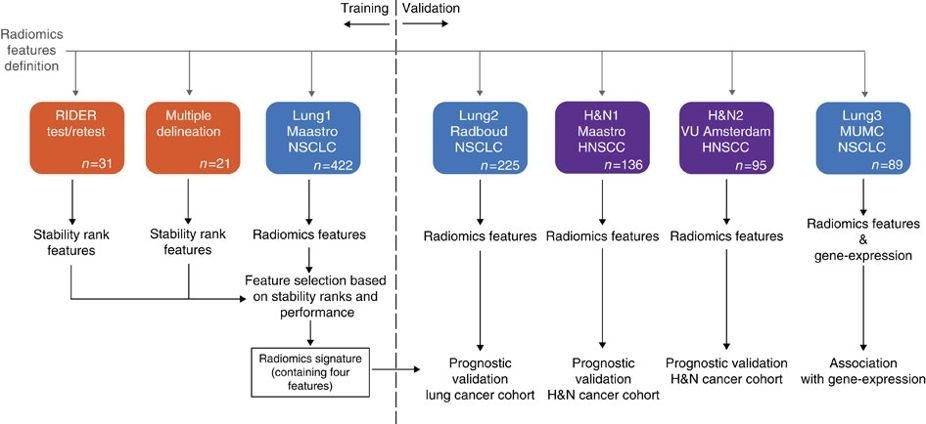
This collection contains clinical data and computed tomography (CT) from 22 non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) radiotherapy patients. For 21 of these patients with pre-treatment CT scans, repeated blinded manual delineations by five different radiation oncologists of the 3D volume of the gross tumor volume on CT and clinical outcome data are available. The above was repeated with the same set of five radiation oncologists, using an in-house autosegmentation tool for initial delineation followed by manual adjustment of the primary gross tumor volume outline. For one patient, clinical data and CT was available but the tumor delineations were not extracted. This patient was included in this collection for the sake of completeness. This dataset refers to the "Multiple delineation" dataset of the study published in Nature Communications (https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms5006). In short, the publication used a radiomics approach to computed tomography data of 1,019 patients with lung or head-and-neck cancer. Radiomics refers to the comprehensive quantification of tumor phenotypes by applying a large number of quantitative image features. In the published analysis, 440 features quantifying tumor image intensity, shape, and texture were extracted. We found that a large number of radiomic features have prognostic power in independent data sets, many of which were not identified as significant before. Radiogenomics analysis revealed that a prognostic radiomic signature, capturing intra-tumor heterogeneity, was associated with underlying gene-expression patterns. These data suggest that radiomics identifies a general prognostic phenotype existing in both lung and head-and-neck cancer. This may have a clinical impact as imaging is routinely used in clinical practice, providing an unprecedented opportunity to improve decision-support in cancer treatment at low cost. The delineations are provided in two formats; DICOM RTSTRUCT contains slice by slice contour points of the external outline of the primary tumour. DICOM SEGMENTATION contains binary masks of the same primary tumour. The nomenclature of the structures are as follows: Side note : Radiation oncologists denoted “1” and “3” were trainee radiation oncologists at the time of this experiment. Radiation oncologists “2”, “4” and “5” were extensively experienced at the time of this experiment. This dataset is intended to be open access to support repeatability and reproducibility of research in the radiomics domain. This dataset has been referenced in Medical Physics Dataset Article addressing FAIR radiomics practices to support transparency, harmonization and collaboration on radiomics (https://doi.org/10.1002/mp.14322). Other data sets in the Cancer Imaging Archive that were used in the same study published in Nature Communications: HEAD-NECK-RADIOMICS-HN1, NSCLC-Radiomics-Interobserver1, NSCLC-Radiomics-Genomics, RIDER-LungCT-Seg. For scientific or other inquiries about this dataset, please contact TCIA's Helpdesk.
Data Access
Version 3: Updated 2020/08/31
Resolved the inadvertent mismatch of the labels between the DICOM Segmentations and the RTSTRUCT annotations. Version 2 was replaced.
| Title | Data Type | Format | Access Points | Subjects | License | Metadata | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Images and Segmentations | RTSTRUCT, CT, SEG | DICOM | Download requires NBIA Data Retriever |
22 | 22 | 64 | 3,886 | CC BY-NC 3.0 | View |
| Clinical Data | Demographic, Diagnosis | CSV | 22 | CC BY-NC 3.0 | — |
Additional Resources for this Dataset
The NCI Cancer Research Data Commons (CRDC) provides access to additional data and a cloud-based data science infrastructure that connects data sets with analytics tools to allow users to share, integrate, analyze, and visualize cancer research data.
- Imaging Data Commons (IDC) (Imaging Data)
Citations & Data Usage Policy
Data Citation Required: Users must abide by the TCIA Data Usage Policy and Restrictions. Attribution must include the following citation, including the Digital Object Identifier:
Data Citation |
|
|
Wee, L., Aerts, H. J.L., Kalendralis, P., & Dekker, A. (2019). Data from NSCLC-Radiomics-Interobserver1 [Data set]. The Cancer Imaging Archive. https://doi.org/10.7937/tcia.2019.cwvlpd26. |
Acknowledgements
We would like to acknowledge the individuals and institutions that have provided data for this collection:
- Leonard Wee, MAASTRO (Dept of Radiotherapy), Maastricht University Medical Centre+, Maastricht, Limburg, The Netherlands.
- Dirk de Ruysscher, MAASTRO (Dept of Radiotherapy), Maastricht University Medical Centre+, Maastricht, Limburg, The Netherlands.
- Andre Dekker, MAASTRO (Dept of Radiotherapy), Maastricht University Medical Centre+, Maastricht, Limburg, The Netherlands.
- Hugo Aerts, Computational Imaging and Bioinformatic Laboratory, Dana-Farber Cancer Institute & Harvard Medical School, Boston, Massachusetts, USA.
- Petros Kalendralis, MAASTRO (Dept of Radiotherapy), Maastricht University Medical Centre+, Maastricht, Limburg, The Netherlands.
- Harmonization of the components of this dataset, including into standard DICOM representation, was supported in part by the NCI Imaging Data Commons consortium. NCI Imaging Data Commons consortium is supported by the contract number 19X037Q from Leidos Biomedical Research under Task Order HHSN26100071 from NCI.
Related Publications
Publications by the Dataset Authors
The authors recommended the following as the best source of additional information about this dataset:
Publication Citation |
|
|
Aerts HJWL, Velazquez ER, Leijenaar RTH, Parmar C, Grossmann P, Carvalho S, Bussink J, Monshouwer R, Haibe-Kains B, Rietveld D, Hoebers F, Rietbergen MM, Leemans CR, Dekker A, Quackenbush J, Gillies RJ, Lambin P. Decoding Tumour Phenotype by Noninvasive Imaging Using a Quantitative Radiomics Approach, Nature Communications, Volume 5, Article Number 4006, June 03, 2014. DOI: http://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms5006. |
Publication Citation |
|
|
Kalendralis, P., Shi, Z., Traverso, A., Choudhury, A., Sloep, M., Zhovannik, I., Starmans, M.P., Grittner, D., Feltens, P., Monshouwer, R., Klein, S., Fijten, R., Aerts, H., Dekker, A., van Soest, J. and Wee, L. (2020). FAIR‐compliant clinical, radiomics and DICOM metadata of RIDER, Interobserver, Lung1 and Head‐Neck1 TCIA collections. Medical Physics. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/mp.14322. |
.
Research Community Publications
TCIA maintains a list of publications that leveraged this dataset. If you have a manuscript you’d like to add please contact TCIA’s Helpdesk.
Previous Versions
Version 2: Updated 2019/10/18
Added DICOM Segmentations for the primary tumor only, the ROI (GTV-1) for the RTSTRUCTs and DICOM Segs are the same.
| Title | Data Type | Format | Access Points | License | Metadata | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Images | RTSTRUCT, CT, SEG | DICOM | Download requires NBIA Data Retriever |
22 | 22 | 64 | 3,886 | — | |
| Clinical Data | CSV | — |
Version 1: Updated 2019/06/02
| Title | Data Type | Format | Access Points | License | Metadata | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Images | RTSTRUCT, CT | DICOM | Download requires NBIA Data Retriever |
22 | 22 | 43 | 3,865 | — | |
| Clinical Data | CSV | — |
