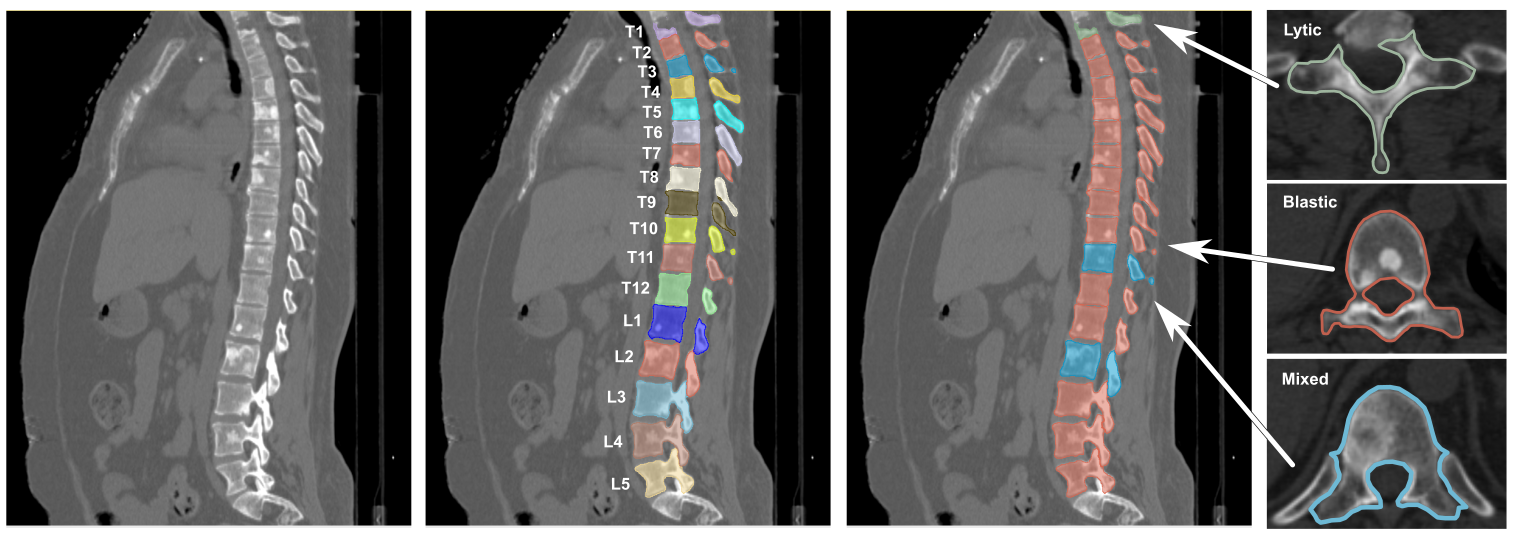
This collection contains subjects from the National Cancer Institute’s Clinical Proteomic Tumor Analysis Consortium Head-and-Neck cancer (CPTAC-HNSCC) cohort. CPTAC is a national effort to accelerate the understanding of the molecular basis of cancer through the application of large-scale proteome and genome analysis, or proteogenomics. Radiology...