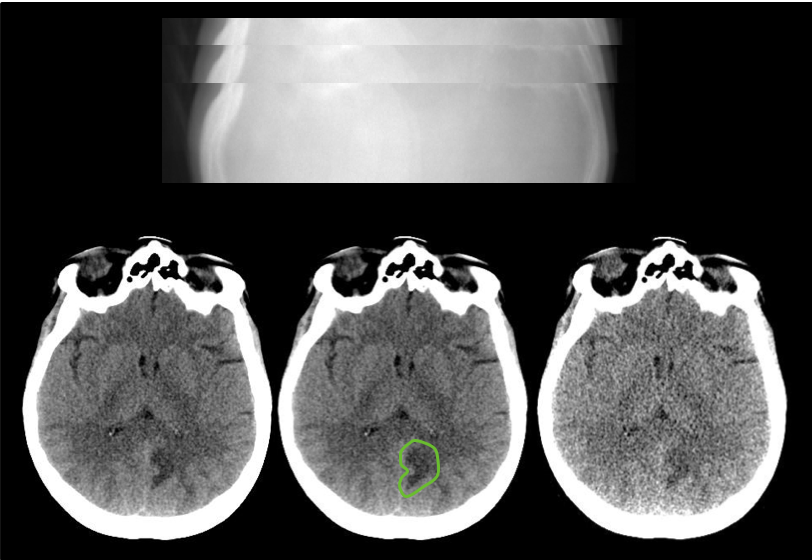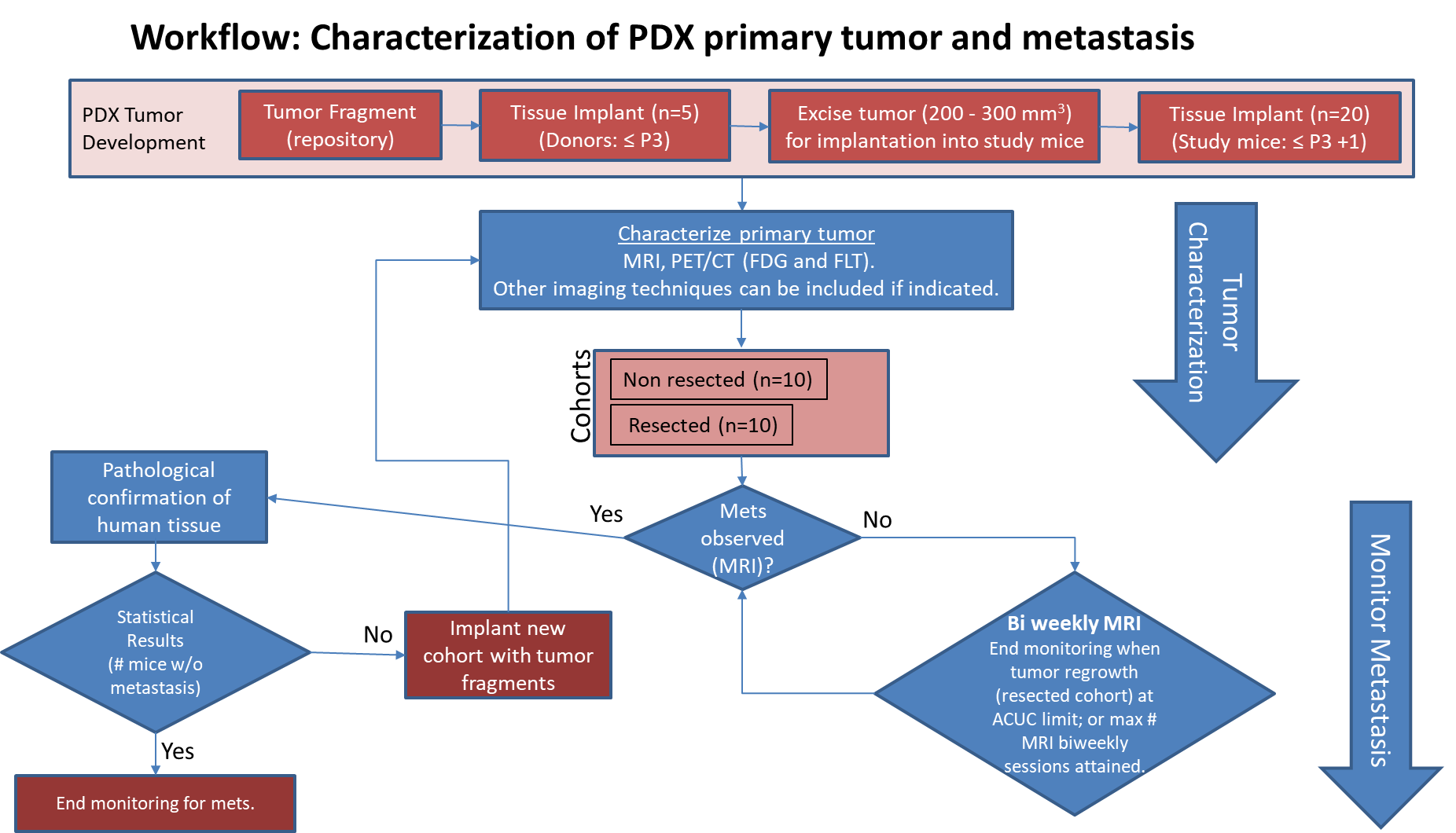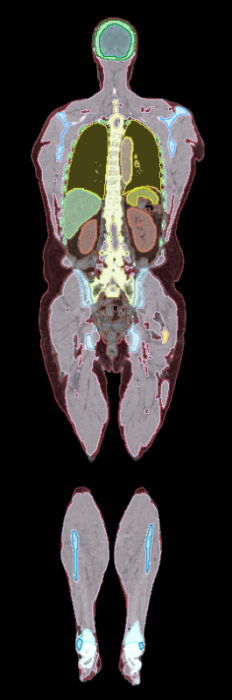
This data set includes low-dose whole body CT images and tissue segmentations of thirty healthy adult research participants who underwent PET/CT imaging on the uEXPLORER total-body PET/CT system at UC Davis. Participants included in this study were healthy adults, 18 years of age or older, who were able to provide informed written consent. The participants' age, sex, weight, height, and body mass index are also provided.
Fifteen...