...
...
The dataset contains a collection of over 170,000 de-identified, expert-annotated cells from the bone marrow smears of 945 patients stained using the May-Grünwald-Giemsa/Pappenheim stain. The diagnosis distribution in the cohort included a variety of hematological diseases reflective of the sample entry of a large laboratory specialized in leukemia diagnostics. Image acquisition was performed using a brightfield microscope...
This collection consists of Computed Tomography (CT) images of the mediastinum and abdomen in which lymph node positions are marked by radiologists at the National Institutes of Health, Clinical Center. Radiologists at the Imaging Biomarkers and Computer-Aided Diagnosis Laboratory labeled a total...
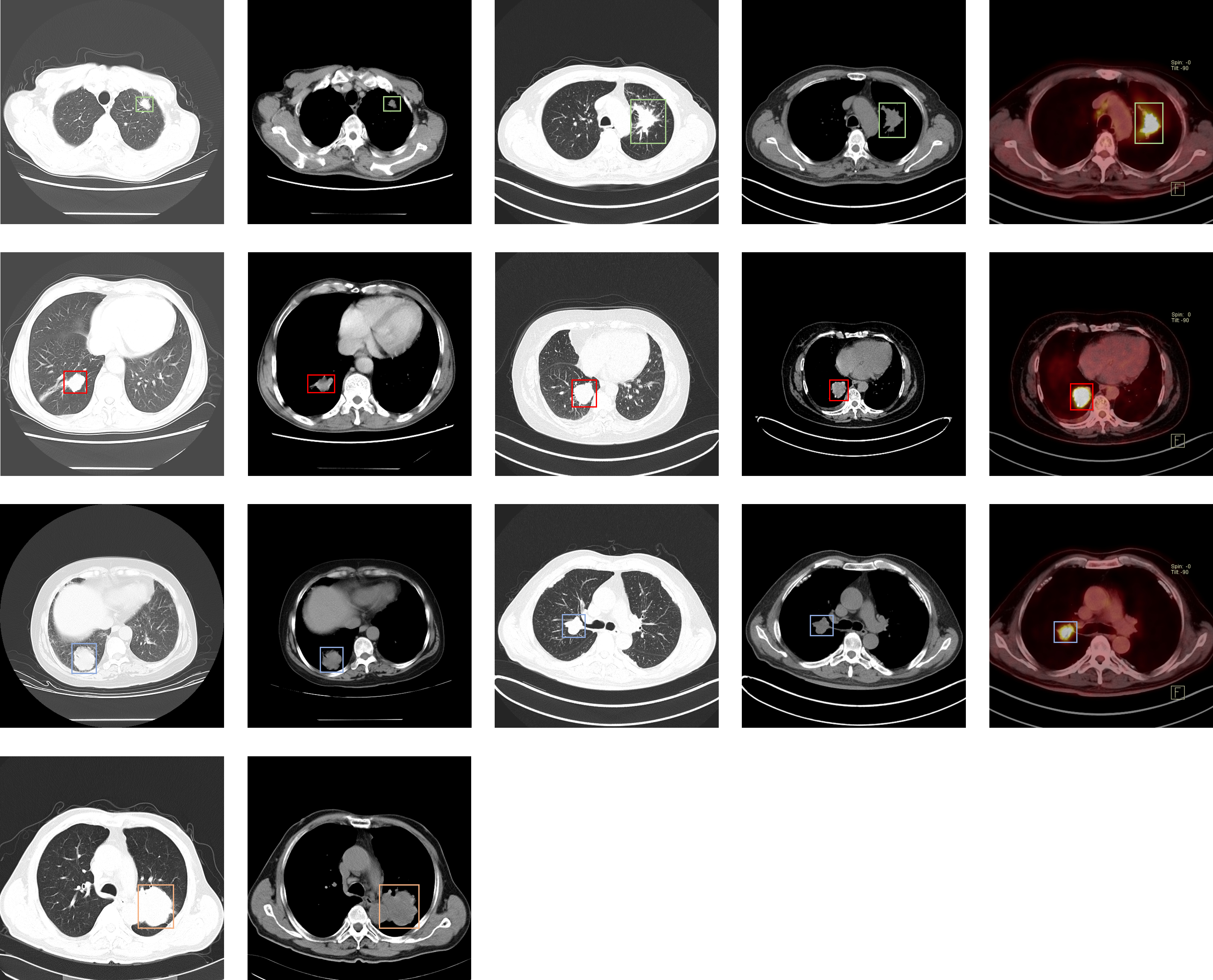
This dataset consists of CT and PET-CT DICOM images of lung cancer subjects with XML Annotation files that indicate tumor location with bounding boxes. The images were retrospectively acquired from patients with suspicion of lung cancer, and who underwent standard-of-care lung biopsy and PET/CT. Subjects were grouped according to a tissue histopathological diagnosis. Patients with Names/IDs containing the letter...
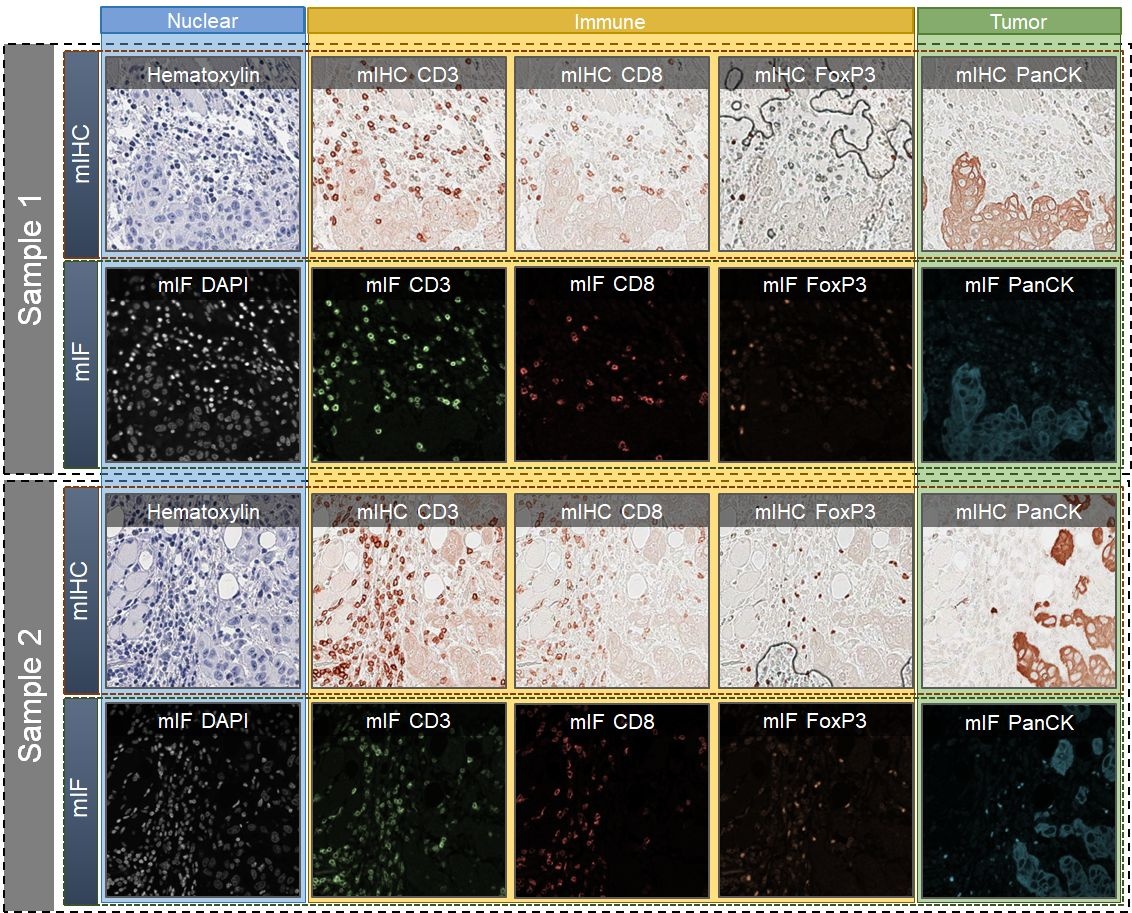
We introduce a new AI-ready computational pathology dataset containing restained and co-registered digitized images from eight head-and-neck squamous cell carcinoma patients. Specifically, the same tumor sections were stained with the expensive multiplex immunofluorescence (mIF) assay first and then restained with cheaper multiplex immunohistochemistry (mIHC). This is a first public dataset that demonstrates...
Open access or shared research data must comply with (HIPAA) patient privacy regulations. These regulations require the de-identification of datasets before they can be placed in the public domain. The process of image de-identification is time consuming, requires significant human resources, and is prone to human error. Automated image de-identification algorithms have been developed but the research community...
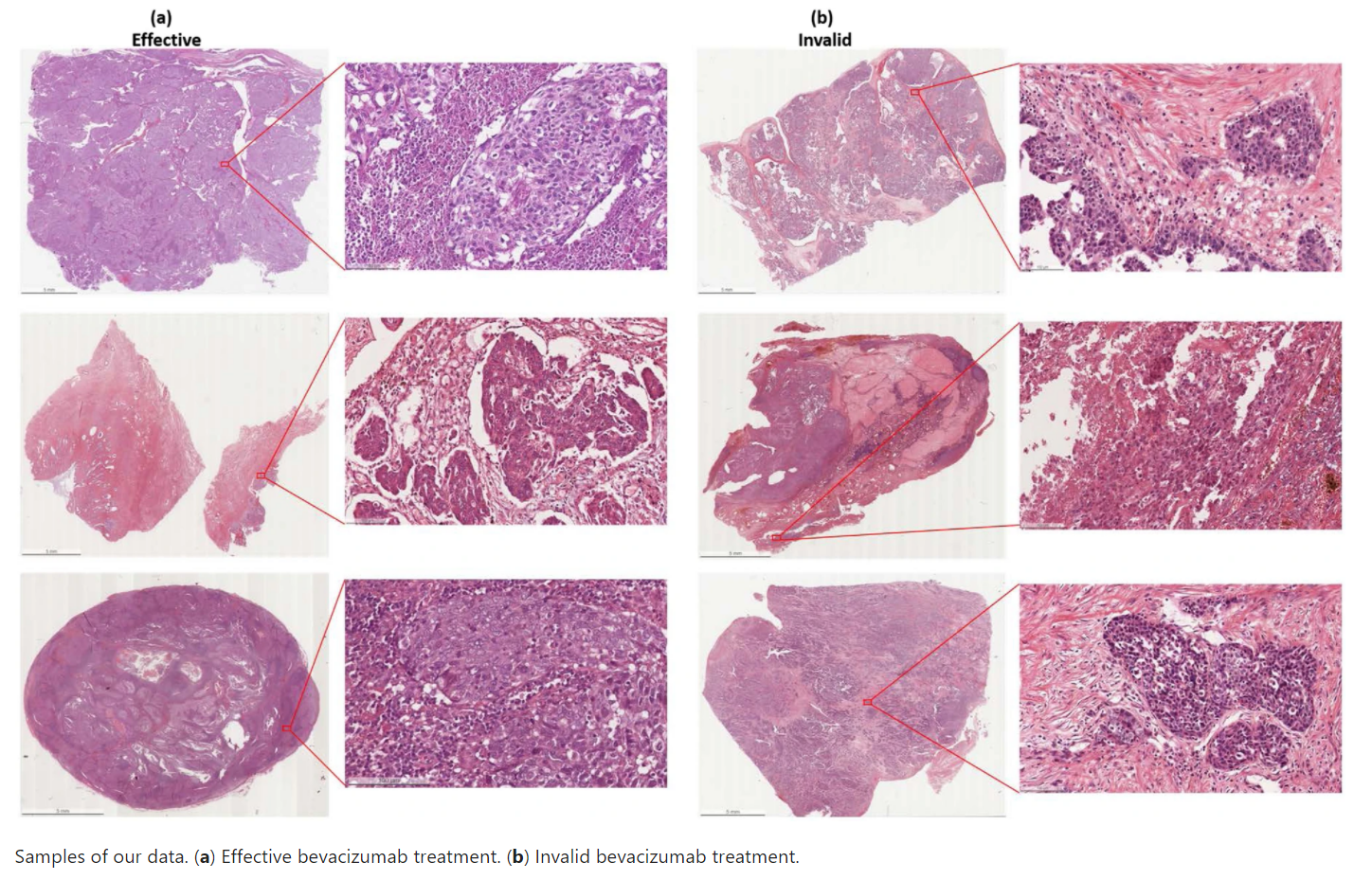
Despite the progress made during the last two decades in the surgery and chemotherapy of ovarian cancer, more than 70% of advanced patients are with recurrent cancer and decease. Bevacizumab has been recently approved by FDA as a monotherapy for advanced ovarian cancer in combination with chemotherapy. Considering the cost, potential toxicity, and finding that only a portion of patients will benefit from...
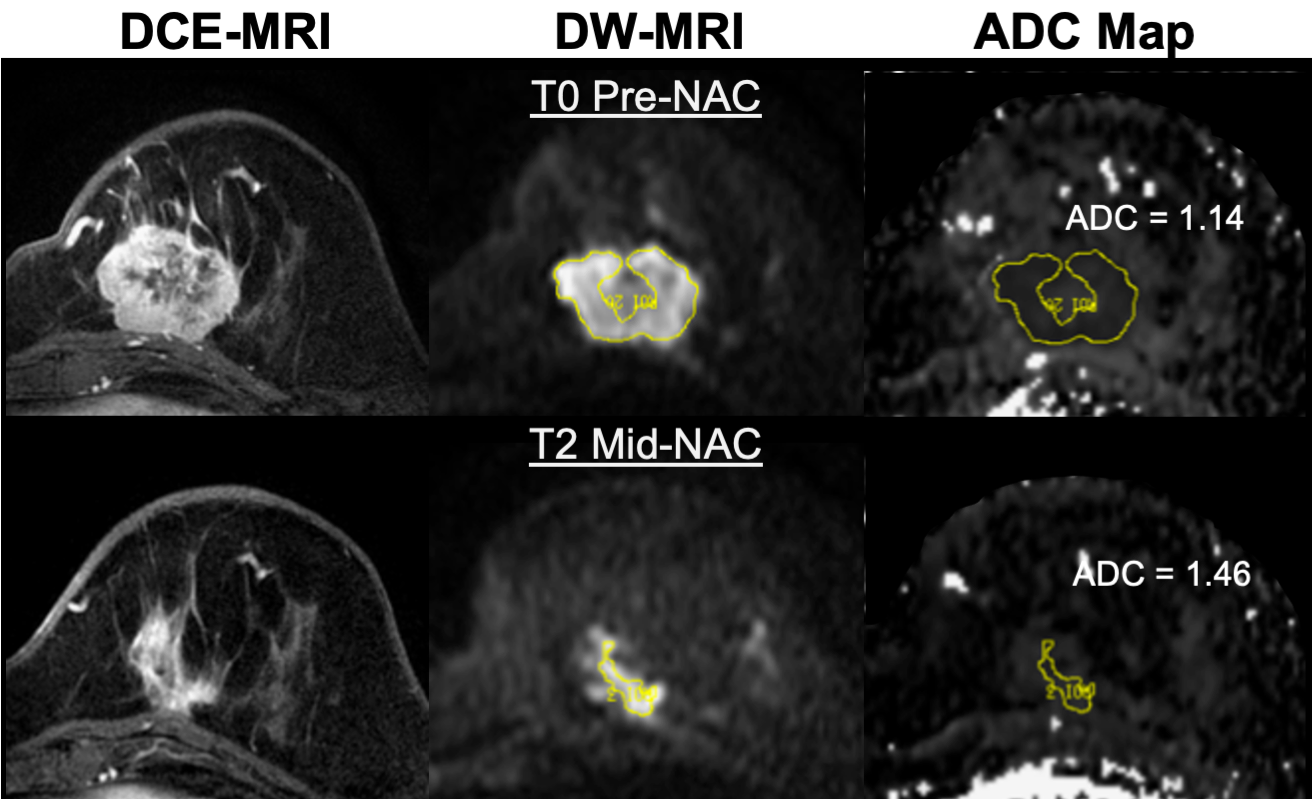
The American College of Radiology Imaging Network (ACRIN) trial 6698 (NCT01564368) was a multi-center study to evaluate the effectiveness of quantitative diffusion weighted imaging (DWI) for assessing breast cancer response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy (NAC). ACRIN 6698 was performed as a sub-study of the ongoing I-SPY 2 TRIAL (Investigation of Serial...
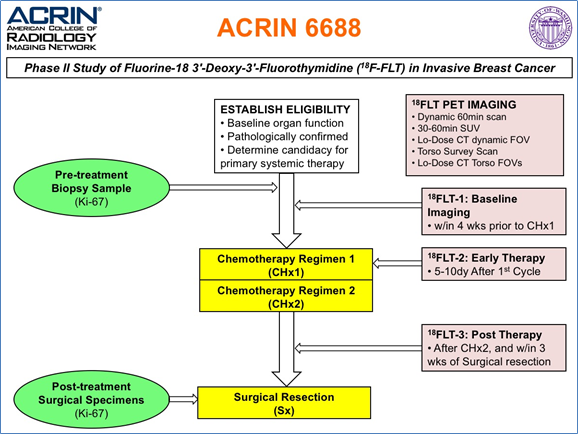
The objective of the ACRIN 6688 multi-center clinical trial was to correlate changes measured by 18F-FLT PET imaging, a measure of cellular proliferation, in the primary tumor early during NAC (neo-adjuvant chemotherapy) with pCR (pathologic complete response) in locally advanced breast cancer patients. The trial also examined both pre-therapy and post-therapy association of 18F-FLT uptake with...
